Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
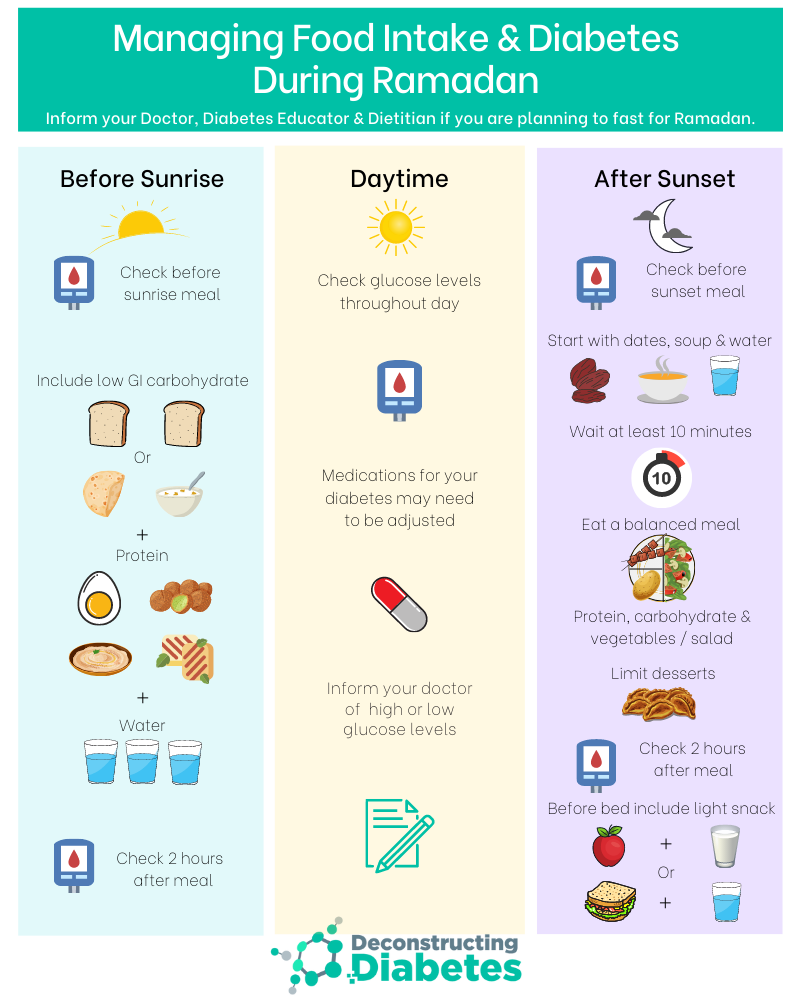
An individualised patient-centric treatment plan is essential to allow both type 1 and type 2 patients to achieve optimal glycaemic outcomes but enable them to observe a risk-free month of fasting during Ramadan. Please refer to specific sick-day rules guidelines in times of illness for drug dose modifications. Key revisions include updates to the risk stratification of individuals with diabetes that are seeking to fast; further evidence on the changes that can occur to the body with Ramadan fasting; new information on pre-Ramadan education and Ramadan Nutrition Plans (RNP). The role of optimum diabetes care in form of Ramadan focused diabetes education, flash glucose monitoring system and pre-Ramadan dose adjustments in the safety of Ramadan fasting in high risk patients with diabetes. It is estimated that about 79% of Muslims with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and about 43% of them with type 1 diabetes (T1D) fast during Ramadan . Of those who fast during Ramadan, 64% fasted every day, and 94.2% fasted for at least 15 days . Get information on diabetes and Ramadan, the risk of fasting also tips if you decide to fast for Ramadan. Ramadan runs from 22 March to 21 April in 2023 The role of optimum diabetes care in form of Ramadan focused diabetes education, flash glucose monitoring system and pre-Ramadan dose adjustments in the safety of Ramadan fasting in high risk patients with diabetes. Ramadan is a time of spiritual reflection and renewal for millions of Muslims worldwide, but for those living with diabetes, fasting presents unique challenges. Successfully navigating this holy month requires careful planning and a proactive approach to managing blood sugar levels. Insulin pumps can potentially empower patients with diabetes and enable safe fasting during the month of Ramadan. Further clinical trials are needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new antidiabetic agents and new diabetes-related technologies during Ramadan. Conclusion: Fasting Safely with Diabetes During Ramadan. Managing diabetes during Ramadan requires a thoughtful approach, balancing fasting glucose management with safe eating habits. By adopting diabetic fasting tips, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adjusting medications, individuals can fast safely while preserving their health. There are potential risks of complications from fasting, such as low or high blood sugar, and dehydration. Typically, people with Type 2 diabetes that is well-controlled, who manage their diabetes with medications and lifestyles, may be OK fasting during Ramadan, so long as they can adjust their medications under the guidance of their care team. Fasting during Ramadan can affect your diabetes management. Talk to your doctor before Ramadan to adjust your medication. Test your blood sugar more often – it doesn't break your fast. Know the signs of hypos (low blood sugar) and treat them immediately if they occur, even if it means breaking Since our last publication about diabetes and fasting during Ramadan (), we have received many inquires and comments concerning important issues that were not discussed in the previous document, including the voluntary 1- to 2-day fasts per week that many Muslims practice throughout the year, as well as the effect of prolonged fasting (more than 18 h a day) in regions far from the equator INTRODUCTION. Fasting the Holy month of Ramadan may be challenging for the people with diabetes and their care providers due to potentially increased risk of acute complications such as hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, dehydration and probably diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), although there is very little evidence that DKA is increased during Ramadan.1 Hence, in 2005, the first statement for You may be advised not to fast if your diabetes management is unstable prior to Ramadan, if you have type 1 diabetes, if you are hypo unaware, pregnant, unwell, or will be performing intense physical labour. The aim of the current study, therefore, was to examine glycemic control among Muslim and Jewish populations with type 2 diabetes – prior to and following the Ramadan fast. We hypothesized that an association would be seen between the Ramadan fast and worsened glycemic control in Muslim participants compared non-Muslim patients. Ramadan is a holy month for all Muslims, when they fast from dawn to sunset. Although the Qur’an exempts the sick from fasting, many Muslims with diabetes passionately fast despite their medical %PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 88 0 obj > endobj xref 88 34 0000000016 00000 n 0000001367 00000 n 0000001494 00000 n 0000002532 00000 n 0000002645 00000 n 0000002681 00000 n 0000005166 00000 n 0000007925 00000 n 0000011177 00000 n 0000014108 00000 n 0000017125 00000 n 0000019500 00000 n 0000019953 00000 n 0000020350 00000 n 0000020820 00000 n 0000021108 00000 n 0000021559 00000 n 0000022091 00000 n Moreover, managing diabetes in fasting Ramadan patients require different mechanisms than the routine diabetes management and pose significant challenge to the health care practitioners. According to the EPIDIAR(Epidemiology of Diabetes and Ramadan) study on 12,243 Muslims from 13 different countries, approximately 43% of Type 1 Diabetes patients and 79% of Type 2 Diabetes patients fast every year during Ramadan. For adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes intending to fast, a pre-Ramadan individualized assessment should be performed 1 to 3 months prior to the start of fasting to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, with maintenance of stable glycemic control [Grade C, Level 3 [13]].
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |