Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
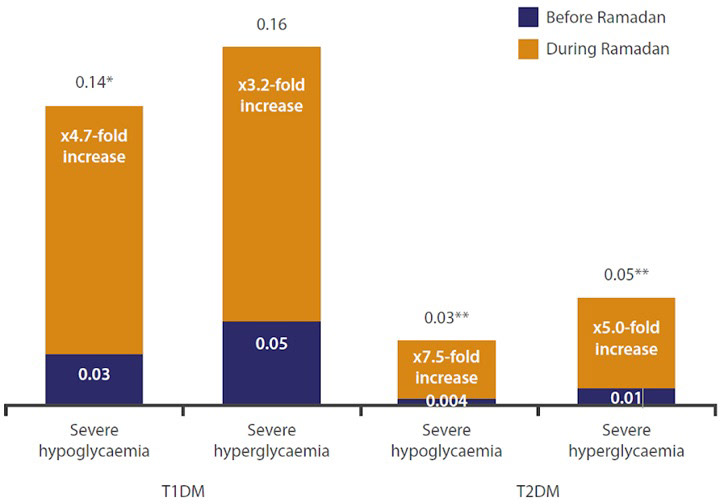
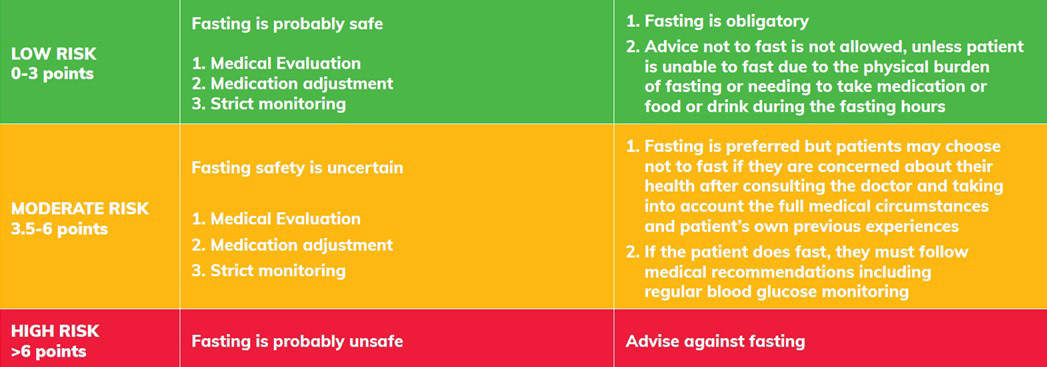
Calculate risk of a person living with diabetes before opting to fast using the 2021, IDF-DAR risk stratification algorithm published in the IDF-DAR Practical Guidelines, chapter 5: Risk stratification of people with diabetes before Ramadan. International Diabetes Federation-Diabetes and Ramadan Alliance (IDF-DAR) Fasting Risk Assessment stratifies fasting risk during Ramadan in diabetic patients. These individuals are at a lower risk of complications arising when fasting during Ramadan. However, circumstances can change leading to a change in the risk scoring. Therefore, risk stratification should be conducted annually to review the level of risk in advance of Ramadan. Calculate risk of a person living with diabetes before opting to fast. 1. Diabetes type and duration. 2. Duration of Diabetes (years) 3. Presence of hypoglycaemia. 4. Level of glycaemic control. 5. Type of treatment. 6. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG) 7. Acute complications. 8. MVD Complications/Comorbidities. 9. providers. However, there is a lack of studies evaluating the impact of Ramadan fasting on various kidney diseases. The Ramadan and Kidney Disease (RaK) working group has developed a risk stratification tool to categorize CKD patients intending to fast into low, moderate, and high-risk groups. We propose a Ramadan fasting calculator Dr Mehjabeen Beebeejaun has designed a risk calculator which she uses in her practice as a guide for both the patient and the healthcare team to predict complications of fasting if a patient has diabetes. Pre-Ramadan assessment in patients with diabetes who want to fast. Pre-assessment should take place 6–8 weeks before Ramadan and should review: Diabetes type and duration; Diabetes medication; Complications and/or comorbidities; Hypoglycaemia risk; Previous experience during Ramadan; Ability to self-manage diabetes; Social and work circumstances Observational studies have shown that people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at risk of hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia during Ramadan. Ramadan-focused structured diabetes educations have also been shown to reduce these risks, and ensure safer fasting during Ramadan. The new IDF-DAR risk calculator is a good tool to predict both the ability to fast Ramadan and the probability of experiencing adverse events (mainly hypoglycemia) in people with diabetes mellitus in Kingdom of Bahrain. The Diabetes and Ramadan Risk Calculator, developed in 2021, is a pivotal tool for assessing fasting-related risks among patients with diabetes. This ground-breaking innovation offers a quantitative assessment of risk scores during fasting, revolutionizing the landscape of diabetes management during Also, in the DAR-BAN study, all 30 days of Ramadan were observed by 71% of the participants; this included 72.8% of those in the moderate-risk group and 49.3% of those in the high-risk group. 5 This suggests that the IDF-DAR stratification score might overestimate the risk of fasting in some diabetics. As Ramadan fasting is compulsory for all There is a high prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Muslim adult patients. Those Muslims are required to fast the holy month of Ramadan. However, the Islam religion exempted some people with medical issues. It was not clear if all the patients with diabetes were considered medically unfit to fast Ramadan. Therefore, IDF-DAR group created a new risk calculator to categorize the patients with Keywords: IDF-DAR risk calculator, T2DM, Ramadan fasting, Fasting complications, Hypoglycemia. Introduction. Worldwide, 537 million adults aged 20–79 had diabetes mellitus (DM) in 2021, most of which were type 2 DM (T2DM) . >200 million Muslims worldwide, and the world’s widespread Muslim population makes up most people in 49 countries . b> Introduction: A novel clinical calculator was developed to assist physicians in classifying the risk for individuals with diabetes planning to observe fasting during the holy month of Ramadan. Methods: We performed a prospective, survey-based study before and after Ramadan 1442/2021 to explore the ability of the new IDF-DAR risk stratification tool to predict the probability of fasting and the risk of complications from fasting in people with diabetes. Aims: To risk-stratify patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to the IDF-DAR 2021 guidelines and observe their responsiveness to risk-category-based recommendations and fasting Objective: To determine the risk status of people with DM who wish to fast during Ramadan Methods: This cross-sectional observational study was done among Muslim people of DM with at least one Objectives: To assess the validity of the new International Diabetes Federation-Diabetes and Ramadan International Alliance (IDF-DAR) risk stratification tool for Ramadan fasting in predicting diabetic patients’ ability to fast safely. Methods: A prospective observational study was carried out during Ramadan 2022 at the Diabetes Center, King Fahad Hospital, Al-Madinah Al-Munawarah, Saudi Conclusion Diabetic patients in the Low-risk category, according to the IDF-DAR risk assessment, had a better outcome than the Moderate or high-risk categories during Ramadan regarding significant Observational studies have shown that people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at risk of hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia during Ramadan. Ramadan-focused structured diabetes educations have also been shown to reduce these risks, and ensure safer fasting during Ramadan.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |