Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
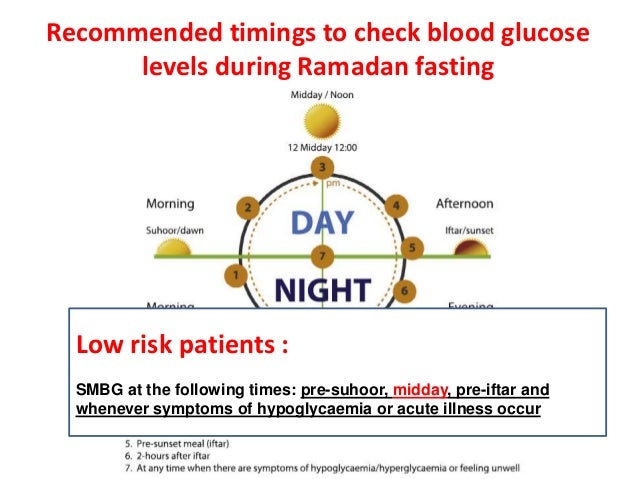
Adjust iftar and suhoor doses according to blood glucose test. Basal rate – Reduce dose by 20–40% in the last 3–4 hours of fasting. Increase dose by 0– 30% early after iftar. General dietary advice for patients with diabetes during Ramadan (IDF 2018). This page has information for people living with diabetes who are thinking about fasting for Ramadan. Ramadan in 2025 will run from on or around Friday 28 February for 29 or 30 days, ending with Eid al-Fitr, a religious holiday celebrated by Muslims worldwide. Insulin pumps can potentially empower patients with diabetes and enable safe fasting during the month of Ramadan. Further clinical trials are needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new antidiabetic agents and new diabetes-related technologies during Ramadan. Conclusion: Fasting Safely with Diabetes During Ramadan. Managing diabetes during Ramadan requires a thoughtful approach, balancing fasting glucose management with safe eating habits. By adopting diabetic fasting tips, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adjusting medications, individuals can fast safely while preserving their health. Fasting during Ramadan can affect your diabetes management. Talk to your doctor before Ramadan to adjust your medication. Test your blood sugar more often – it doesn't break your fast. Know the signs of hypos (low blood sugar) and treat them immediately if they occur, even if it means breaking Key revisions include updates to the risk stratification of individuals with diabetes that are seeking to fast; further evidence on the changes that can occur to the body with Ramadan fasting; new information on pre-Ramadan education and Ramadan Nutrition Plans (RNP). A significant number of individuals with diabetes fast during Ramadan, even against medical advice and despite the religious exemptions available to the sick (1, 30, 33). This population also includes adolescents with T1D, who fast against medical advice . Ramadan is a time of spiritual reflection and renewal for millions of Muslims worldwide, but for those living with diabetes, fasting presents unique challenges. Successfully navigating this holy month requires careful planning and a proactive approach to managing blood sugar levels. The role of optimum diabetes care in form of Ramadan focused diabetes education, flash glucose monitoring system and pre-Ramadan dose adjustments in the safety of Ramadan fasting in high risk patients with diabetes. The role of optimum diabetes care in form of Ramadan focused diabetes education, flash glucose monitoring system and pre-Ramadan dose adjustments in the safety of Ramadan fasting in high risk patients with diabetes. Fasting during Ramadan can affect your diabetes management. Talk to your doctor before Ramadan to adjust your medication. Test your blood sugar more often – it doesn't break your fast. Know the signs of hypos (low blood sugar) and treat them immediately if they occur, even if it means breaking Although physicians often recommend refraining from Ramadan fasting for individuals with diabetes, many choose to observe the fast, due to religious considerations . According to one report, 64 % of patients with type 2 diabetes were found to fast for all 30 days of the Ramadan, with 94 % fasting for at least 15 days. The landmark Epidemiology of Diabetes and Ramadan (EPIDIAR) study found that as many as 42.8% of the 1080 patients with T1 diabetes and 78.7% of the 11,173 patients with T2 diabetes reported fasting for at least 15 days during Ramadan , leading to an estimation that approximately 120 million people with diabetes worldwide fast during Ramadan Moreover, managing diabetes in fasting Ramadan patients require different mechanisms than the routine diabetes management and pose significant challenge to the health care practitioners. You may be advised not to fast if your diabetes management is unstable prior to Ramadan, if you have type 1 diabetes, if you are hypo unaware, pregnant, unwell, or will be performing intense physical labour. Objective This systematic review and meta-analysis assess the effects of Ramadan fasting in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), on blood sugar factors such as hemoglobin A1C and problems caused by its lack of control such as hypoglycemia and DKA, and metabolic outcomes. Methods Electronic databases including MEDLINE, Embase, and SINOMED were searched up to February 13, 2024 Non-insulin-dependent medications like sodium-glucose-cotransporter-2 inhibitors, including the Food and Drug Administration-approved ertugliflozin, are also being used to provide additional cardiovascular benefits in patients with type 2 diabetes. Keywords: Ramadan, Fasting, Diabetes, Complications, Insulin therapy, Newer advances, Hypoglyccemia For adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes intending to fast, a pre-Ramadan individualized assessment should be performed 1 to 3 months prior to the start of fasting to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, with maintenance of stable glycemic control [Grade C, Level 3 [13]]. Patients with diabetes, especially those with type 1 diabetes, who fast during Ramadan, are at increased risk for development of diabetic ketoacidosis, particularly if their diabetes is poorly controlled before Ramadan . In addition, the risk for diabetic ketoacidosis may be further increased due to excessive reduction of insulin dosages based Fasting the month of Ramadan is a fundamental religious practice performed by millions of Muslims every year. Fasting Ramadan has been shown to be associated with an increased risk of hypoglycemia and glycemic deterioration in some patients with diabetes, particularly type1 diabetes , .
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |