Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
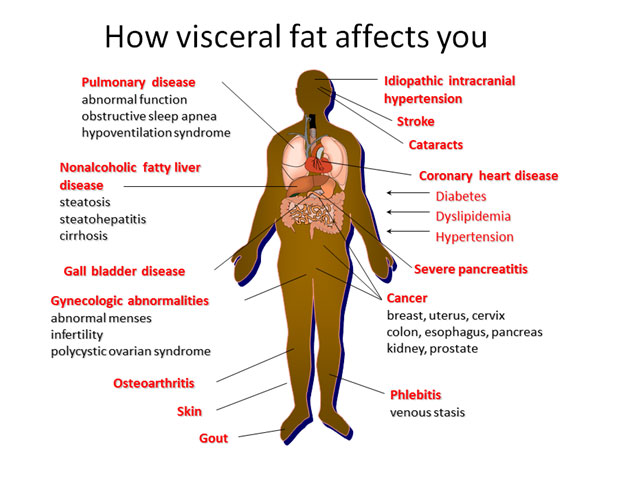
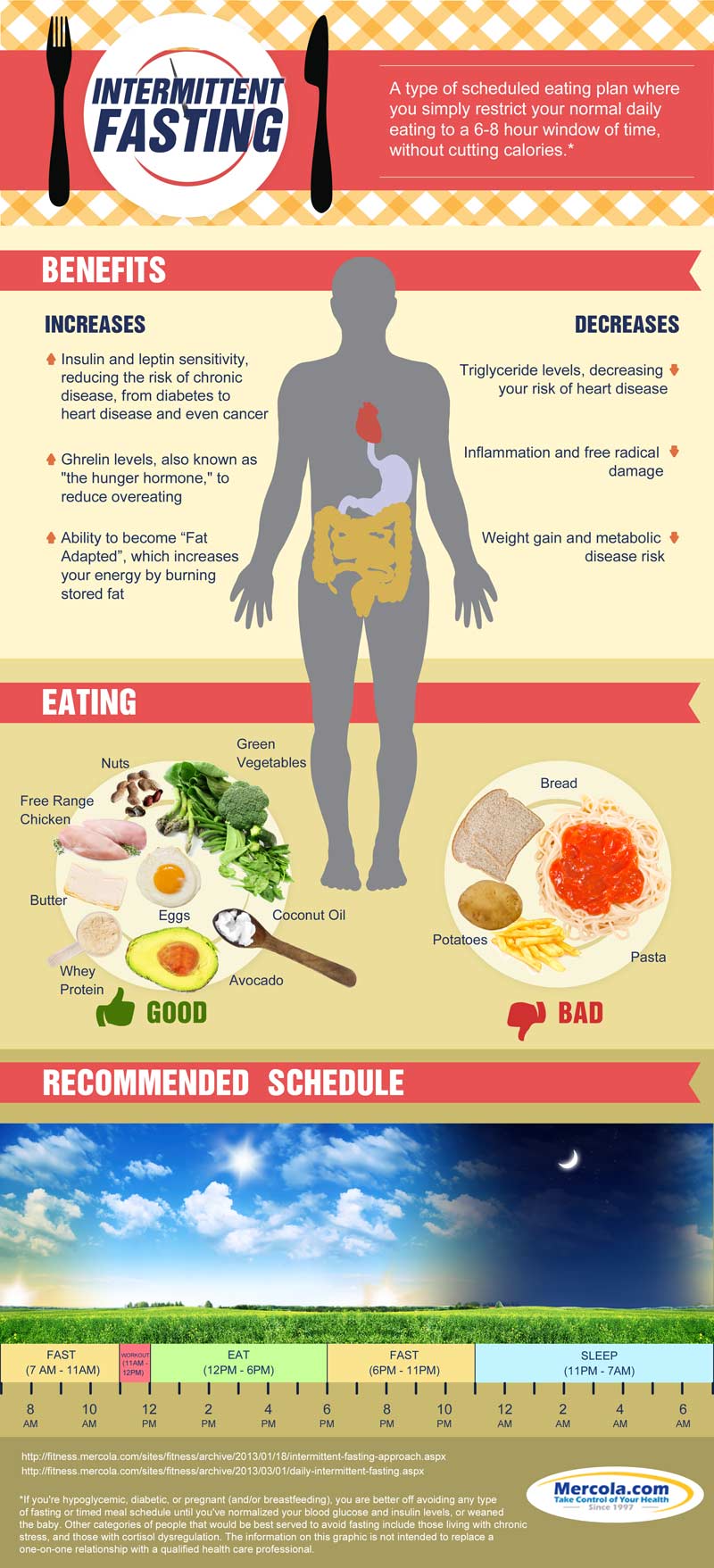
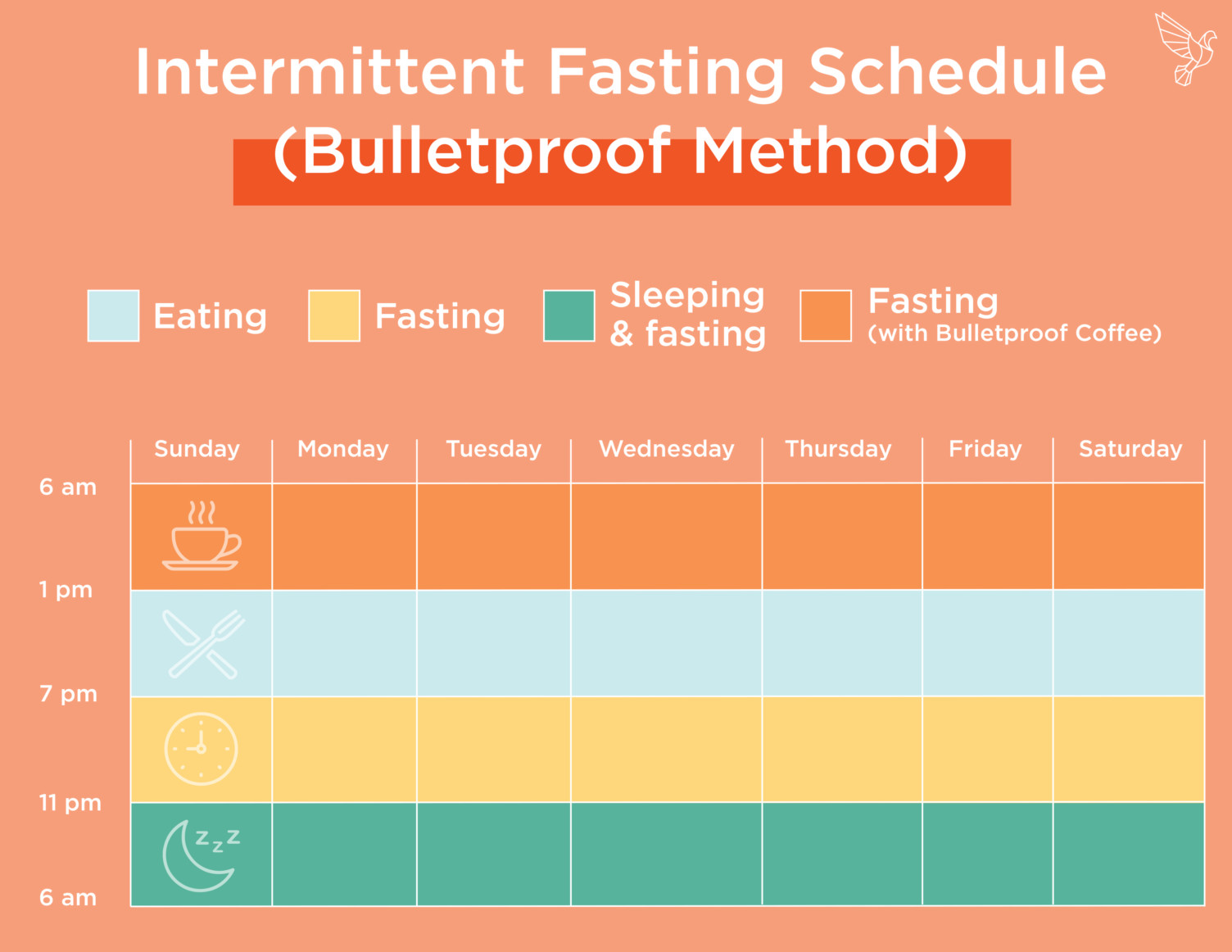
Methods: In 21 healthy Muslims, we assessed the impact of RIF on caloric intake, physical activity, gastrointestinal symptoms and motility (gastric/gallbladder emptying by ultrasonography, orocaecal transit time by lactulose breath test), anthropometric indices, subcutaneous and visceral fat thickness (ultrasonography), glucose and lipid We studied the effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting (RIF) on gut hormones (leptin, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), peptide YY (PYY), cholecystokinin (CCK), and ghrelin) in males with Overall, fasting patterns during Ramadan can improve gastrointestinal motility associated with the MMC, allowing intestinal contents to move efficiently through the GI tract. Additionally, fasting allows the gut to cleanse and strengthen its lining. Ramadan Intermittent fasting (RIF) exerts beneficial metabolic effects and improves gastrointestinal motility. However, a comparison between RIF and the traditional 16-hours intermittent fasting (16IF), a strategy for weight loss, is lacking. Intermittent fasting during Ramadan attenuates proinflammatory cytokines and immune cells in healthy subjects. Alternate day calorie restriction improves clinical findings and reduces markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in overweight adults with moderate asthma. Both Ramadan and non-Ramadan intermittent fasting are effective on fat mass and body weight losses. Fat mass loss is more pronounced with non-Ramadan intermittent fasting and this type of intermittent fasting, combined with exercise training, leads to higher decreases in body mass index. Background. Ramadan is a model of intermittent fasting linked with possible beneficial effects. Scarce information, however, is available about the combined effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting (RIF) on anthropometric and metabolic indices, gastrointestinal symptoms, and motility. Both 16IF and RIF are able, during 1-month, to reduce body weight. However, RIF but not 16IF also generates marked beneficial effects in terms of reduced subcutaneous fat and liver steatosis. Further studies urge to verify the effects of different models of IF in weight-cycling and long-term managem Previous evidence from our group showed that RIF has beneficial effects in terms of reduced body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, fasting serum glucose, serum insulin and grade of insulin resistance, decreased subcutaneous and visceral fat, and improved gastrointestinal motility [8]. Changes induced by fasting schemes positively impact the diversity and abundance of gut microbiota and the biomarkers described here, however, the changes previously reported have been studied in short periods and some return to their basal state after fasting intervention. Obesity often results in severe negative health consequences and represents a growing issue for global health. Reducing We are approaching aspects of intermittent fasting (IF) from different perspectives and studies. We previously reported that Ramadan IF reduces visceral fat and improves gastrointestinal motility . Here , we confirmed these findings while implementing the biophysical characterization of fat and comparing Ramadan IF (RIF) with 16-hour IF (16IF). <span> <h5>Background</h5> <p>Ramadan is a model of intermittent fasting linked with possible beneficial effects. Scarce information, however, is available about the Obesity is a metabolic disease characterized by fat over-storage in multiple districts. The continuous increase of the obesity epidemic makes mandatory innovative interventions and new guidelines to manage weight gain [1]. Besides reduced energy intake increased physical activity, pharmacological interventions, and bariatric surgery or endoscopy, a critical role is played by the timing of Background Ramadan is a model of intermittent fasting linked with possible beneficial effects. Scarce information, however, is available about the combined effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting (RIF) on anthropometric and metabolic indices, gastrointestinal symptoms, and motility.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |